JavaScript全解析——node介绍
node 的概念
●什么是 node?
○官方原话:
■一个基于 Chrome V8 解析引擎的 JavaScript 运行时环境
○换句话说:
■从前有一个人, 把浏览器内的 JS 解析引擎拿出来, 和其它内容进行了一个组装
■变成了一个新的东西, 并起了个名字叫做: 'NodeJS'
●前端 JS 和 NodeJS 的区别 1
○前端 JS
■当 JS 被引入到 HTML 文件中, 放在浏览器中执行的时候 (JS 的组成: BOM + DOM + ECMAScript)
■他在这个时候, 才会有所谓的 BOM 和 DOM
●BOM: 浏览器对象模型 浏览器提供给我们的
●DOM: 文档对象模型 HTML 提供给我们的
○NodeJS
■把 JS 从 HTML 文件中拿出来, 放在 电脑系统中直接运行
■此时没有所谓的 DOM 和 BOM
■但是因为是在 电脑系统中运行
●可以操作 文件/文件夹 (I/O; input/output)
●可以操作电脑系统
●可以操作数据库
●...
●前端 JS 和 NodeJS 的区别 2
○前端 JS
■运行时可以操作模块发开发(ES6 模块化), 也可以采用非模块开发
■为什么可以采用非模块化
■因为我们把所有的 JS 文件, 引入到某一个 HTML 文件中, 去使用
○ NodeJS
○运行时 必须采用 模块化开发
○因为他是直接执行 JS 文件, 没有一个统一的 html 文件去引入所有的 JS 文件
○使用的 模块化语法 是 CommonJS
●JS 代码种是没有错误的
○关键是我们要把 JS 运行在那个环境(要把代码运行在哪里)
○假设 将来需要把这个 JS 文件放在前端使用(引入到 HTML, 并运行在浏览器中)
■那么可以在 JS 中书写 BOM 和 DOM 相关的东西
○ 假设 将来需要把这个 JS 文件放在 NODEJS 中使用
■那么就不能在 JS 中书写 DOM 和 BOM 相关的 东西
■但是 此时可以书写 操作 文件/文件夹相关的代码
●NodeJS 的作用
○按照 CommonJS 模块化开发语法的规范进行书写代码
○能够 使用 JS 这个语言 进行后端代码的开发
node 初体验
●如何利用 node 执行 JS 代码
○因为 node 是直接在电脑操作系统上进行 JS 代码的执行
○其实就是 在 小黑窗 内直接执行 JS 文件
○小黑窗内执行 JS 代码
■方式 1:
●打开 小黑窗, 目录无所谓
●输入命令: node 按下回车
●会进入 JS 代码编辑模式
○此时是不能执行 cmd 命令的, 只能书写 JS 代码
●按下 ctrl + c 退出当前环境
●缺点: 书写的代码无法保存
■方式 2:
●把你要执行的 JS 代码 书写在一个 .js 文件内
●打开命令行, 切换目录到 JS 文件所在的目录
●输入指令: node 文件名
内置模块
node 的模块化开发
●node 必须模块化开发
●node 自带的所有内容都是以模块的形式出现的
● 模块化语法
○导出
■每一个 JS 文件天生自带一个变量叫做 module
■表示的是当前自己这个模块的所有信息
■ 每一个文件默认导出一个对象
■语法:
●如果你想向默认导出的对象内添加成员
●module.exports.属性名 = 属性值
●exports.属性名 = 属性值
●node 的 每一个 JS 文件, 内部天生自带一个 变量 叫做 exports
● 变量内部存放的是 指向 module.exports 这个对象的 地址
■如果你想修改这个默认导出的内容
●module.exports = 值
○导入
■ 每一个 JS 文件天生自带一个方法叫做 require()
■语法: require('地址')
●注意: 如果地址书写的时候, 文件后缀是 .js, 那么可以省略后缀不写
■返回值: 该文件的 module.exports (该文件向外暴露的内容)
●模块分类
○自定义模块
■自己写的 JS 文件
○内置模块
■node 给我们提供的模块, 直接引入使用即可
○第三方模块
■由其他人写好上传到某一个仓库内(npm)
■我们去这个仓库内(npm)下载到本地, 然后引入使用
●node 内置模块 fs
node 给出的内置模块, 专门用来操作 文件/文件夹
1.异步读取文件
a.语法: fs.readFile(文件路径, 配置参数, 回调函数)
b.参数:
i.文件路径: 必填
ii.配置参数: 不写默认是 buffer 可以手动配置为 utf-8
iii.回调函数: 必填, 接受两个参数, 第一个为报错信息, 第二个为正确读取到的文件的内容(字符串格式的)
fs.readFile("./index1.txt", "utf-8", (error, data) => {
if (error) return console.log(error);
console.log(data);
});
同步读取文件
let str = fs.readFileSync("./index1.txt", "utf-8");
console.log(str);
2.异步写入文件
a.语法: fs.writeFile(文件地址, 写入内容, 回调函数)
b.参数:
i.文件地址:
1.这个文件, 直接讲内容写入到指定文件内
2.没有这个文件, 创建一个出来, 然后写入到指定文件内
ii.写入内容:
1.符串格式的内容, 将这段文本直接写入到指定文件中, 并覆盖这个文件之前的所有内容
iii.回调函数:
1.必写, 哪怕这个函数什么也不做, 也必须要写
fs.writeFile("./index.txt", "你好 世界", () => {
console.log("写入完成");
});
同步写入文件
fs.writeFileSync("./index.txt", "hello word");
console.log("node end");
●node 内置模块 path
node 自带的模块, 专门用于和路径相关的操作
1.绝对路径
a.C:/a/b/c/d.html
2.相对路径
a. ./d.html
b. ../c/d.html
●组装一个相对路径 path.join(路径片段 1, 路径片段 2, 路径片段 3)
const res = path.join("a", "b/c", "d", "e.html");
console.log(res); // a\b\c\d\e.html
●组装一个绝对路径 path.resolve(路径片段 1, 路径片段 2, 路径片段 3)
const res1 = path.resolve("a", "b/c", "d", "e.html");
const res2 = path.resolve("C:", "b/c", "d", "e.html");
console.log(res1); // C:\Users\41099\Desktop\qianfeng-prepares-lessons\06_周\05_天\code\06_内置模块path\a\b\c\d\e.html
console.log(res2); // D:\b\c\d\e.html
●组装一个解析路径 path.parse(路径)
const res = path.parse(
"C:/Users/41099/Desktop/qianfeng-prepares-lessons/06_周/05_天/code/06_内置模块path/a/b/c/d/e.html"
);
console.log(res);
/*
{
// 根路径
root: 'C:/',
// 完整文件目录(截止到目录, 不会到文件)
dir: 'C:/Users/41099/Desktop/qianfeng-prepares-lessons/06_周/05_天/code/06_内置模块path/a/b/c/d',
// 完整文件名
base: 'e.html',
// 文件后缀名
ext: '.html',
// 文件名
name: 'e'
}
*/
●node 内置模块 url
node 自带的模块, 专门用来操作 url 地址的
●url.parse('地址', 是否深度解析);
○地址: 必填
○是否深度解析
■ 默认是 false, 不深度解析, 可以手动配置为 true
■深度解析其实就是把 对象中的 query 解析为 对象格式
const res = url.parse(
"http://www.baidu.com:8080/a/b/c/index.html?key=value&name=QF001&age=18#abc",
true
);
console.log(res);
/*
Url {
// 协议
protocol: 'http:',
slashes: true,
auth: null,
// 域(域名+端口号)
host: 'www.baidu.com:8080',
// 端口号
port: '8080',
// 域名
hostname: 'www.baidu.com',
// hash值
hash: '#abc',
// 携带的参数
search: '?key=value&name=QF001&age=18',
// 查询字符串
query: 'key=value&name=QF001&age=18',
// 路径名称
pathname: '/a/b/c/index.html',
// 路径(路径名称 + 参数)
path: '/a/b/c/index.html?key=value&name=QF001&age=18',
// 完整地址
href: 'http://www.baidu.com:8080/a/b/c/index.html?key=value&name=QF001&age=18#abc'
}
深度解析后的
Url {
...
query: [Object: null prototype] { key: 'value', name: 'QF001', age: '18' },
...
}
*/
●node 内置模块 http
node 自带的一个模块, 用于开启一个 http 服务
●服务器
○提供 服务 的 机器
■服务: 提供一些内容(文件/数据)
■机器: 电脑
○有一台电脑, 运行了 一个 '软件'
■ 这个 "软件" 可以向外开放一个 "文件夹"(根目录)
■当其他电脑访问到这台电脑的时候, 并且制定了访问这个 "软件" 的时候
■那么相当于在访问这个文件夹
○例子:
■一台电脑: 10.11.12.13
■软件: 8080
■开放的文件夹是: D:/a/b
■当你打开浏览器访问 http:10.11.12.13:8080 的时候, 就是在访问这台电脑上的 D:/a/b
○node 就可以利用 http 模块来充当 "软件" 启动服务
1.创建服务
a.语法: http.createServer(函数)
b.函数: 每当前端有一个请求访问这个服务器的时候, 就会执行一次
- 返回值: 一个服务
const http = require('http')
const server = http.createServer(() => {
console.log("前端发一次请求, 我就执行一次");
});
2.给当前服务配置一个端口号
a.语法: server.listen(端口号(0~65535), 回调函数)
const http = require('http')
const server = http.createServer(() => {
console.log("前端发一次请求, 我就执行一次");
});
server.listen(8080, () => {
console.log("启动服务成功~~~");
});
3.创建函数时 函数接收的两个参数
a.第一个 形参: request, 对应的值为前端请求时携带的请求报文
b.第二个 形参: response, 表示本次响应的相关信息, 你只要添加到 res 内, 会由服务器自动组装响应报文返回给前端
const http = require('http')
const server = http.createServer((request, response) => {
if (request.url === "/a") {
response.end("hello pageA");
}
if (request.url === "/b") {
response.end("hello pageB");
}
});
server.listen(8080, () => {
console.log("启动服务成功~~~");
});
补充---请求
●什么算请求?
○在浏览器地址栏输入一个 地址, 然后按下回车
■以浏览器为主体在发送请求
■服务器返回的内容直接给到浏览器, 显示在页面上
○在浏览器内 以 link script iframe img 等标签请求的内容
■例如:
■例如:
○当前页面中的 js 代码内的 ajax 请求
●请求的完整地址是什么
○在一个 html 文件内所有的书写地址的位置都可以写 绝对地址 和 相对地址
■绝对地址: 写什么就是什么
■ 相对地址: 你打开的文件地址是什么, 那么相对地址就按照打开文件的地址进行拼接
○例子: 打开页面是 http://localhost:8080/a/b/c/index.html
■如果你的地址写的是 ./a/a.css
●完整地址: http://localhost:8080/a/b/c/a/a.css
■你的地址写的是 ../a.css
●完整地址: http://localhost:8080/a/b/a.css
■你的地址写的是 ../d/a.css
●完整地址: http://localhost:8080/a/b/d/a.css
■你的地址写的是 /a.css
●完整地址: http://localhost:8080/a.css
搭建简易服务器
1.初始搭建
// 0. 导入模块
const http = require("http");
const url = require("url");
const fs = require("fs");
// 1. 创建服务
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
// 1.1 解析 url
const { query, pathname } = url.parse(req.url, true);
if (pathname === "/a") {
// 如果访问的是 /a 那么读取 client目录下的views目录下的pageA.html 并返回出去
fs.readFile("./client/views/pageA.html", "utf-8", (err, data) => {
if (err) return console.log(err);
res.end(data);
});
}
if (pathname === "/b") {
res.end("hello pageB");
}
if (pathname === "/list") {
// 如果访问的是 /list 那么读取 client目录下的views目录下的list.html 并返回出去
fs.readFile("./client/views/list.html", "utf-8", (err, data) => {
if (err) return console.log(err);
res.end(data);
});
}
});
// 2. 给服务配置端口号
server.listen(8080, () => console.log("开启服务成功, 端口号为 8080"));
2.配置 css
// 0. 导入模块
const http = require("http");
const url = require("url");
const fs = require("fs");
const path = require("path");
// 1. 创建服务
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
const { query, pathname } = url.parse(req.url, true);
/**
* 约定
* 如果请求的 地址 是以 /views 开头
* 表明你需要访问的是 html 文件, 后续写上 html 文件名即可
* 比如你要请求 home.html
* => 请求地址: /views/home.html
*/
if (/^\/views/.test(pathname)) {
// 代码来到这里, 表明我们需要的是一个 html 文件
// console.log(pathname)
const { base } = path.parse(pathname);
fs.readFile(`./client/views/${base}`, "utf-8", (err, data) => {
if (err) {
fs.readFile("./client/views/404.html", "utf-8", (err, data) => {
if (err) return console.log(err);
res.end(data);
});
return;
}
res.end(data);
});
}
/**
* 约定
* 如果请求的地址 是以 /style 开头
* 表明你需要访问的是 css 文件, 后续写上 css 文件名即可
* 比如你要请求 list.css
* => 请求地址 /style/list.css
*/
if (/^\/style/.test(pathname)) {
// 代码来到这里, 表明我们需要的是一个 css 文件
const { base } = path.parse(pathname);
fs.readFile(`./client/css/${base}`, "utf-8", (err, data) => {
if (err) {
res.end("");
return;
}
res.end(data);
});
}
});
// 2. 给服务配置端口号
server.listen(8080, () => console.log("开启服务成功, 端口号为 8080"));
3.接口和静态资源
// 0. 导入模块
const http = require("http");
const url = require("url");
const fs = require("fs");
const path = require("path");
// 1. 创建服务
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
const { query, pathname } = url.parse(req.url, true);
/**
* 约定
* => 把 html/css/js/img/video/audio/icon 叫做 静态资源
* => 只要你请求的是 静态资源, 统一以 /static 开头
* => 只要你请求的是 接口数据, 统一以 /api 开头
*/
// 1. 判断当前请求的是静态资源
if (/^\/static/.test(pathname)) {
// 1.1 解析 pathname
const { base, ext } = path.parse(pathname);
// 1.2 通过 后缀名 和 base, 确定读取文件的路径
let filePath = "./client/";
switch (ext) {
case ".html":
filePath += "views/";
break;
case ".css":
filePath += "css/";
break;
case ".js":
filePath += "js/";
break;
}
// 1.3 拼接 base
filePath += base; // ./client/views/list.html
// 2. 读取文件
fs.readFile(filePath, "utf-8", (err, data) => {
if (err) {
if (ext === ".html") {
// 返回 404 文件
fs.readFile("./404.html", "utf-8", (err, data) => {
if (err) return console.log(err);
res.end(data);
});
} else {
res.end("");
}
return;
}
res.end(data);
});
}
// 2. 判断当前请求的是 接口数据
if (/^\/api/.test(pathname)) {
if (pathname === "/api/goods/list" && req.method === "GET") {
// 如果 当前请求的 地址 是 '/api/goods/list' 并且是 GET 请求
// 去数据库读取数据, 返回给前端
const info = {
code: 1,
message: "从数据库读取数据成功",
list: [{}, {}, {}],
};
res.end(JSON.stringify(info));
}
}
});
// 2. 给服务配置端口号
server.listen(8080, () => console.log("开启服务成功, 端口号为 8080"));
4.接受请求参数
// 0. 导入模块
const http = require("http");
const url = require("url");
const fs = require("fs");
const path = require("path");
// 1. 创建服务
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
/**
* 假设: 你是一个 带有参数的 GET 请求
* http://localhost:8080/api/news/list?current=1&pagesize=12%date=20221127
* 被 url.parse 方法解析
* pathname => /api/news/list
* query => { current: 1, pagesize: 12, date; 20221127 }
*/
const { query, pathname } = url.parse(req.url, true);
// 1. 判断当前请求的是静态资源
if (/^\/static/.test(pathname)) {
// 1.1 解析 pathname
const { base, ext } = path.parse(pathname);
// 1.2 通过 后缀名 和 base, 确定读取文件的路径
let filePath = "./client/";
switch (ext) {
case ".html":
filePath += "views/";
break;
case ".css":
filePath += "css/";
break;
case ".js":
filePath += "js/";
break;
}
// 1.3 拼接 base
filePath += base; // ./client/views/list.html
// 2. 读取文件
fs.readFile(filePath, "utf-8", (err, data) => {
if (err) {
if (ext === ".html") {
// 返回 404 文件
fs.readFile("./404.html", "utf-8", (err, data) => {
if (err) return console.log(err);
res.end(data);
});
} else {
res.end("");
}
return;
}
res.end(data);
});
}
// 2. 判断当前请求的是 接口数据
if (/^\/api/.test(pathname)) {
if (pathname === "/api/goods/list" && req.method === "GET") {
// 如果 当前请求的 地址 是 '/api/goods/list' 并且是 GET 请求
// 去数据库读取数据, 返回给前端
const info = {
code: 1,
message: "从数据库读取数据成功",
list: [{}, {}, {}],
};
res.end(JSON.stringify(info));
}
// 获取get请求的参数
if (pathname === "/api/news/list" && req.method === "GET") {
const info = { code: 1, message: "获取新闻列表成功" };
if (!query.current) {
info.code = 0;
info.message = "没有 current 参数";
} else if (!query.pagesize) {
info.code = 0;
info.message = "没有 pagesize 参数";
} else if (!query.date) {
info.code = 0;
info.message = "没有 date 参数";
} else {
// 表示参数不缺
info.list = [{}, {}, {}, {}];
info.params = query;
}
res.end(JSON.stringify(info));
}
// 获取post请求的参数
if (pathname === "/api/users/login" && req.method === "POST") {
/**
* 需要的参数有两个 username 和 password
* 事件1: req.on('data', () => {})
* 只要请求体内有信息, 就会开始接收, 并且是逐步接收
* 事件2: req.on('end', () => {})
* 当请求体内的参数接受完毕, 触发
*/
let str = "";
req.on("data", (chunk) => (str += chunk));
req.on("end", () => {
/**
* 世界规范:
* 要么传递查询字符串, 要么传递 json 字符串
* 我们只需要按照 查询字符串的格式, 或者 json 字符串的格式解析参数即可
* 要求就是前端在请求头中告诉我们按照什么格式解析字符串
* 世界规范:
* 在请求头中通过 content-type 告诉后端按照什么格式解析参数
* 如果 content-type 值为 application/x-www-form-urlencoded 那么按照 查询字符串解析
* 如果 content-type 值为 application/json 按照 json 字符串解析
*/
let params = null;
if (req.headers["content-type"] === "application/json") {
// 按照 json 的格式转换
params = JSON.parse(str);
}
if (
req.headers["content-type"] ===
"application/x-www-form-urlencoded"
) {
// 按照 查询字符串 的格式转换
params = url.parse("?" + str, true).query;
}
const info = {
code: 1,
message: "请求成功",
params,
};
res.end(JSON.stringify(info));
});
}
}
});
// 2. 给服务配置端口号
server.listen(8080, () => console.log("开启服务成功, 端口号为 8080"));

猜你喜欢LIKE
相关推荐HOT
更多>>
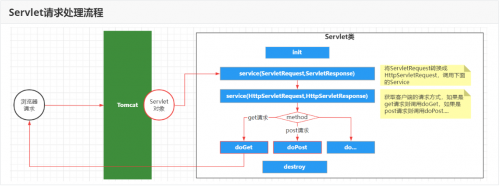
servlet底层原理是什么?
1、ServletAPI核心类与接口2、Servlet类处理请求的流程创建servlet类的步骤:创建一个命名为TestServlet继承javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet类详情>>
2023-05-30 10:41:22
多线程的优势与劣势分别是什么?
多线程是指在同一个程序中,同时运行多个线程,每个线程都可以独立执行不同的任务,相互之间不会干扰。多线程的优势和劣势如下:优势:提高程序...详情>>
2023-05-30 10:32:12
设计模式之生产者与消费者的代码实现
本文主要讲述生产者和消费者模式,文中会使用通俗易懂的案例,使你更好地学习本章知识点并理解原理,做到有道无术。什么是生产者和消费者模式生...详情>>
2023-05-30 10:25:46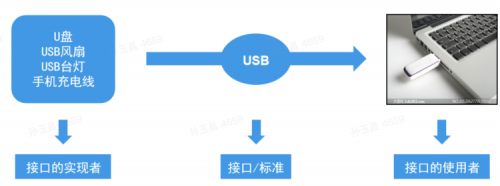
从零开始学Java之interface接口
一.接口简介简介Java中的接口(interface)类似于是一种特殊的抽象类,它也是众多抽象方法的集合。接口的定义方式、组成部分都与抽象类相似,却比...详情>>
2023-05-29 11:26:17热门推荐
如何进行mysql数据备份?
沸什么是servlet的生命周期?servlet请求处理流程是怎样的?
热servlet底层原理是什么?
热怎样编写java程序?
新多线程的优势与劣势分别是什么?
ssm框架的作用与原理是什么?
设计模式之生产者与消费者的代码实现
接口和抽象类有什么区别?4个方面对比
从零开始学Java之interface接口
从零开始学Java之Java中的内部类是怎么回事?
一分钟带你了解MySQL——基础与介绍
在java中,super关键字怎样使用
什么是事件流以及事件流的传播机制 ?
弹性盒有哪些属性是在父元素身上?
技术干货

























 京公网安备 11010802030320号
京公网安备 11010802030320号